- IELTS WRITING TASK 1 - PROCESS DIAGRAM
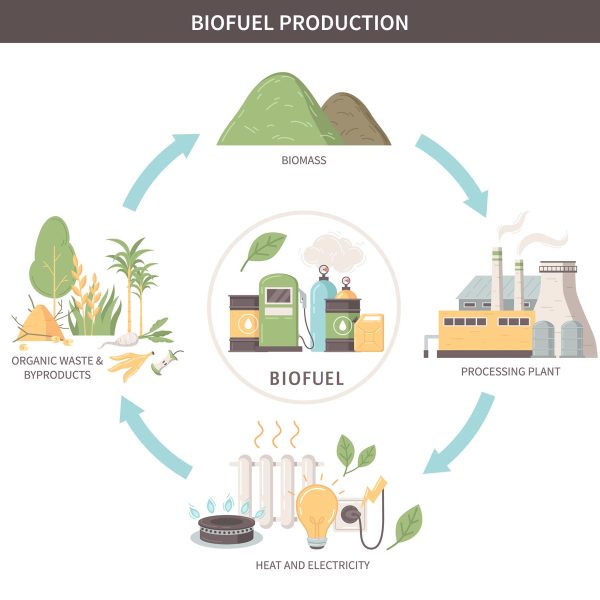
BIOFUEL PRODUCTION PROCESS
You should spend about 20 minutes on this task.
Task: The diagram illustrates the process of biofuel production, from the collection of organic waste and products to the generation of heat and electricity. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Write at least 150 words.
Designed by macrovector | Freepik
Sample Answer, C1 English Level, Advanced, Band Score 6.5-7.5
Biofuel manufacturing entails a succession of well-planned procedures, each of which contributes to the manufacture of sustainable energy. The process begins with the gathering of organic waste and products. These are the raw materials used in the biofuel manufacturing process. After being gathered, these materials are transformed into biomass, which is an important intermediate step. The energy content of biomass is increased by various ways such as the use of anaerobic digestion or fermentation.
Subsequently, the biomass undergoes meticulous processing at a dedicated plant. This stage involves refining the biomass into biofuel through processes like distillation, transesterification, or pyrolysis. This transformed biofuel becomes a renewable energy source that can be harnessed for various purposes.
The culmination of this process lies in the generation of both heat and electricity. Biofuels, when combusted, release energy in the form of heat, which can be used for heating systems. Additionally, biofuels can be employed in power generation, contributing to sustainable electricity production.
In a nutshell biofuel manufacturing is a process that begins with biological waste and ends with the generation of heat and power. From collection to processing, each stage represents a step forward in utilizing renewable energy sources and lowering environmental effects.
There are several crucial steps in the manufacture of biofuels that help to produce sustainable energy. The trip starts with the gathering of organic items and garbage, which serve as the process’s initial raw ingredients. Dedicated energy crops, food scraps, and agricultural residues are a few examples of these.
Following collecting, these materials are converted into biomass. In this step, the organic matter is broken down through anaerobic digestion or fermentation to boost its energy content and make it suitable for the generation of biofuels.
The next phase takes place at a processing plant, where the biomass is converted into biofuel. This involves various techniques such as chemical reactions or heating to extract the energy-rich components. The resulting biofuel can be in the form of bioethanol, biodiesel, or biogas.
The culmination of this process is the utilization of the produced biofuel. It can be burned to generate heat, used in vehicles as an alternative to fossil fuels, or converted into electricity through combustion or other energy conversion methods.This multi-step process contributes to sustainable energy production and reduces the reliance on conventional fossil fuels.
Biofuel production initiates with the gathering of organic waste and resources. These serve as the fundamental building blocks, sourced from agricultural residues, food scraps, or specifically cultivated energy crops. Once collected, these materials undergo a transformative process, turning into biomass. This conversion, often facilitated by methods like fermentation or anaerobic digestion, enhances their energy content, making them suitable for biofuel production.
Subsequently, the transformed biomass is transported to a specialized processing plant. Here, through a range of intricate techniques, such as chemical reactions or heating, the biomass is converted into valuable biofuel. The resulting biofuel can manifest as bioethanol, biodiesel, or biogas, depending on the processing methods employed.
The ultimate fruition of this elaborate process lies in the utilization of the produced biofuel. It can be employed in various domains – from being burned to generate heat for residential or industrial purposes to serving as an eco-friendly alternative in vehicles, thus reducing the reliance on traditional fossil fuels. Moreover, biofuels can also be harnessed to generate electricity, contributing to cleaner energy production.
This intricate progression embodies the synergy between scientific innovation and environmental consciousness, shaping a greener and more sustainable energy landscape.

